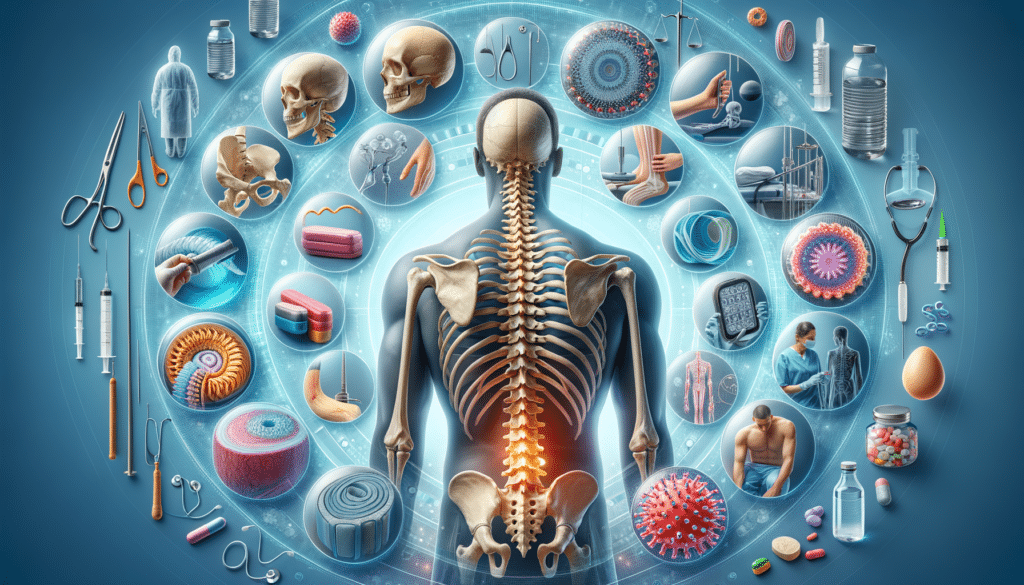
Understanding Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis is a medical condition characterized by the narrowing of spaces within the spine, which can lead to pressure on the spinal cord and nerves. This condition is most commonly found in the lower back and neck. The symptoms can range from mild discomfort to severe pain, numbness, and muscle weakness, significantly affecting a person’s daily activities. Understanding the causes and symptoms of spinal stenosis is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Several factors contribute to the development of spinal stenosis, including age-related changes, arthritis, herniated discs, and congenital spinal deformities. As people age, the wear and tear on the spine can lead to the thickening of ligaments and the growth of bone spurs, which can narrow the spinal canal. Recognizing these contributing factors is essential for both prevention and management.
Symptoms of spinal stenosis vary depending on the location and severity of the narrowing. Common symptoms include:
- Back or neck pain: Persistent pain in the affected area.
- Numbness or tingling: Sensations in the arms or legs.
- Weakness: Muscle weakness, especially in the legs, affecting mobility.
- Balance problems: Difficulty maintaining balance, increasing the risk of falls.
Understanding these symptoms helps in early detection and treatment, which can prevent further complications and improve quality of life.
Non-Surgical Treatments for Spinal Stenosis
Non-surgical treatments are often the first line of defense against spinal stenosis. These treatments focus on alleviating symptoms and improving function without the need for invasive procedures. They are particularly beneficial for individuals with mild to moderate symptoms.
Physical therapy is a cornerstone of non-surgical treatment. A structured exercise program can help strengthen the muscles supporting the spine, improve flexibility, and enhance overall mobility. Physical therapists tailor exercises to individual needs, ensuring that patients can manage their symptoms effectively.
Medications also play a crucial role in managing spinal stenosis. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used to reduce inflammation and relieve pain. In some cases, doctors may prescribe muscle relaxants or nerve pain medications to address specific symptoms.
Epidural steroid injections can provide relief for individuals experiencing severe pain. These injections deliver corticosteroids directly to the affected area, reducing inflammation and alleviating pain. While the effects are temporary, they can provide significant relief and improve quality of life.
Non-surgical treatments are often accompanied by lifestyle modifications. Maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, and avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms are essential components of a comprehensive treatment plan.
Surgical Options for Spinal Stenosis
When non-surgical treatments fail to provide adequate relief, surgical intervention may be considered. Surgery aims to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves by widening the spinal canal. Various surgical options are available, depending on the severity and location of the stenosis.
Laminectomy is the most common surgical procedure for spinal stenosis. It involves removing the lamina, a part of the vertebra, to create more space in the spinal canal. This procedure can effectively relieve pressure on the nerves and alleviate symptoms.
Foraminotomy is another surgical option that involves enlarging the foramen, the opening where nerve roots exit the spinal canal. This procedure is particularly useful for individuals with foraminal stenosis, where nerve compression occurs at these openings.
In some cases, spinal fusion may be necessary to stabilize the spine. This procedure involves joining two or more vertebrae to prevent movement and provide stability. While effective, spinal fusion can limit flexibility and is typically reserved for severe cases.
Minimally invasive surgical techniques have gained popularity in recent years. These procedures involve smaller incisions, leading to shorter recovery times and reduced risk of complications. Patients considering surgery should discuss the potential benefits and risks with their healthcare provider to make an informed decision.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
In addition to conventional medical treatments, alternative and complementary therapies can play a supportive role in managing spinal stenosis. These therapies focus on holistic approaches to health and can enhance overall well-being.
Acupuncture, an ancient Chinese practice, involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to alleviate pain and promote healing. Many individuals with spinal stenosis report significant pain relief and improved function after acupuncture sessions.
Chiropractic care is another popular complementary therapy. Chiropractors use manual manipulation to adjust the spine and improve alignment. While some individuals find relief through chiropractic care, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider to ensure its suitability for spinal stenosis.
Massage therapy can help reduce muscle tension and improve circulation, providing relief from pain and discomfort. Regular massage sessions can enhance relaxation and contribute to overall well-being.
Yoga and tai chi are gentle forms of exercise that focus on flexibility, balance, and mindfulness. These practices can improve posture, enhance mobility, and reduce stress, making them valuable additions to a comprehensive treatment plan.
While alternative therapies can offer benefits, they should be used in conjunction with conventional treatments and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Living with Spinal Stenosis: Tips and Strategies
Living with spinal stenosis can be challenging, but with the right strategies, individuals can manage their symptoms and maintain a fulfilling life. Here are some practical tips for living with spinal stenosis:
- Stay active: Engage in regular physical activity to maintain strength and flexibility. Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling are low-impact options that can improve overall fitness.
- Practice good posture: Maintain proper posture while sitting, standing, and walking to reduce strain on the spine.
- Use supportive devices: Consider using assistive devices such as a cane or walker to enhance stability and reduce the risk of falls.
- Manage stress: Incorporate stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or mindfulness to improve overall well-being.
- Seek support: Join support groups or connect with others living with spinal stenosis to share experiences and gain valuable insights.
By adopting these strategies, individuals with spinal stenosis can improve their quality of life and continue to engage in activities they enjoy. It is essential to work closely with healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses individual needs and goals.